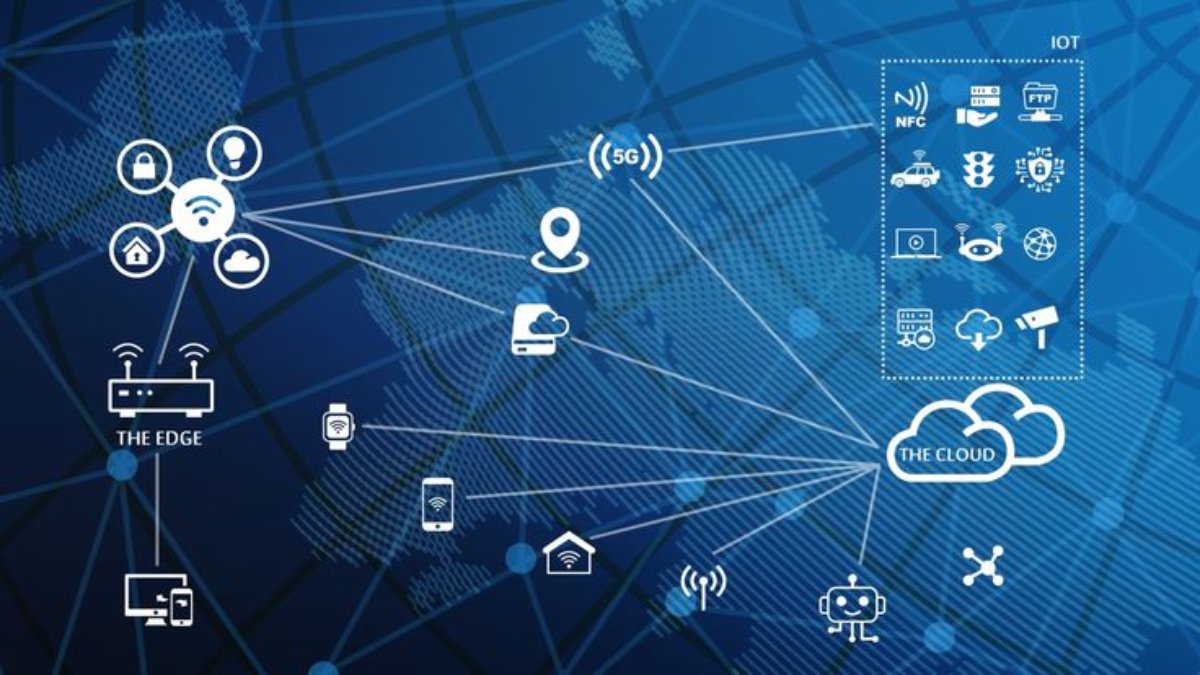
Technology is updating fast. Businesses are adapting to new computing models. This helps them improve efficiency, scalability, and performance. Two dominant approaches have emerged in recent years: edge computing vs cloud computing. Both focus on improving data processing and storage. However, they have different goals and fit specific needs better. Understanding the differences between cloud infrastructure and edge computing helps businesses, IT professionals, and tech enthusiasts choose the best solution for their needs.
This article compares edge computing vs. cloud computing. We’ll look at their key differences, benefits, challenges, and uses. This will help you make better choices.
Looking for ways to leverage AI for the growth of your business? Look no further!
What Is Cloud Computing?

Cloud computing delivers computing services—including storage, processing power, databases, networking, and software—over the internet. Instead of relying on local servers or personal devices, users can access and manage data and applications remotely through cloud service providers like AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud.
Key Characteristics of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing relies on remote data centres to store and process information. It offers scalability, enabling businesses to adjust computing power based on demand. Cloud services can be accessed remotely from anywhere with an internet connection, making them ideal for remote work and collaboration. Many cloud providers use a pay-as-you-go model. This means they charge users based on how much they use. So users don’t have to make big upfront investments.
Types of Cloud Infrastructure
Cloud computing is classified into three main models.
- The public cloud offers many services from experts like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud. These offerings are not only cost-effective but also accessible to all.
- The private cloud creates a bespoke cloud sanctuary crafted exclusively for one organisation. This setup affords greater control over security and customisation, making it a fortress of data.
- The hybrid cloud elegantly combines public and private cloud solutions. It helps businesses share data and applications easily in both areas, unlocking new flexibility.
Advantages of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing brings a treasure trove of advantages for modern businesses.
- First and foremost, it delivers cost efficiency—goodbye to hefty infrastructure investments!
- It also offers disaster recovery solutions, safeguarding data with reliable backups.
- Plus, it champions collaboration and accessibility, letting teams unite across distances in real time.
With the cloud, you’re not just computing; you’re soaring into the future!
Challenges of Cloud Computing
Despite its benefits, cloud computing has some drawbacks.
- Latency issues can appear when data travels to faraway servers, causing delays.
- Security threats lurk in the cloud; if unguarded, data can be compromised.
- Plus, cloud computing demands a steadfast internet connection; disruption spells disaster for businesses.
What Is Edge Computing?
Edge computing is a decentralised computing model that processes data closer to its source rather than relying on a centralised cloud. This approach reduces latency, improves real-time processing, and enhances efficiency for applications like IoT, autonomous vehicles, and smart cities.
Key Characteristics of Edge Computing
Edge computing handles data close to where it’s generated. This includes IoT devices, sensors, and local servers. It cuts down on the need for constant cloud connections. It significantly lowers latency, ensuring faster response times for real-time applications. Edge computing saves bandwidth and prevents network congestion. It does this by processing data right at the source.
Types of Edge Computing
Edge computing unfolds in an array of innovative forms.
- IoT Edge improves the data tools by processing information from nearby IoT devices. This approach sends only the essentials skyward to the cloud.
- Mobile Edge computing turbocharges real-time processing for on-the-go users. Enjoy faster, smoother app experiences and enhanced service performance.
- Fog Computing emerges as a bridge, blending cloud and edge computing seamlessly. It skillfully distributes workloads, striking the perfect balance between efficiency and performance.
Advantages of Edge Computing
Edge computing is a game changer, turbocharging technology with lightning speed and security.
- It slashes latency, perfect for real-time applications like autonomous vehicles and smart cities.
- Security gets a boost, processing data locally and shielding it from cyber dangers.
- Plus, it cuts cloud costs, minimising data transfers and slashing bandwidth bills.
In this new frontier, efficiency and safety meet, creating a smarter digital ecosystem.
Challenges of Edge Computing
Edge computing is a double-edged sword, slicing through challenges and advantages alike.
- Initial Investments can pinch the pocketbook; businesses must fund edge devices and infrastructure.
- Management Mayhem looms large; keeping a distributed network requires time and talent.
- Scalability Snags can hinder growth, demanding extra hardware and management finesse.
Edge Computing vs Cloud: Key Differences

As technology advances, businesses must choose between cloud computing and edge computing for data processing. While cloud computing centralises data in remote servers, edge computing processes data closer to the source, reducing latency and enhancing real-time decision-making.
Data Processing Location
Cloud computing handles data in remote data centres. In contrast, edge computing processes data nearer to the source, at the network edge.
Latency and Speed
Cloud computing often has higher latency. This is because data takes time to travel to centralised servers. Edge computing reduces latency by processing data locally, leading to quicker response times.
Scalability
Cloud computing is highly scalable, allowing businesses to adjust resources based on demand. Edge computing has limited scalability. To expand edge networks, you need to invest in more infrastructure.
Security and Privacy
Cloud computing uses outside servers. These servers can be at risk from cyber threats if they aren’t secured well. Edge computing improves security by processing data locally, reducing exposure to potential breaches.
Connectivity Dependency
Cloud computing needs a stable internet connection to work well. In contrast, edge computing can work with little or no internet. This makes edge computing great for remote areas and important applications.
Real-world Applications of Edge and Cloud Computing
Edge and cloud computing power a wide range of industries, from healthcare and autonomous vehicles to smart cities and IoT devices. While cloud computing enables large-scale data storage and AI processing, edge computing ensures real-time analytics and faster response times in critical applications.
Cloud Computing Use Cases
Cloud computing rules industries that require unlimited storage, easy scaling, and seamless collaboration.
- Enterprise software leaders like Google Workspace and Microsoft 365 rely on cloud technology for seamless operations.
- Streaming services like Netflix, YouTube, and Spotify use the cloud to share content globally.
- E-commerce giants like Amazon and Shopify use cloud servers. They manage transactions and customer connections effectively.
Edge Computing Use Cases
Edge computing shines brightly for applications craving lightning-fast processing and minimal latency.
- Autonomous vehicles use their power to make quick decisions. This cuts the need for remote data centres.
- Smart cities use edge computing to improve traffic flow, boost surveillance, and optimise energy distribution.
- Healthcare solutions, such as remote patient monitoring and AI-driven diagnostics, rely on fast data at the edge. This speed helps provide timely medical responses that can save lives.
Click Here to learn the best practices for preventing cyber attacks.
The Future of Computing Models
As technology evolves, computing models will continue to adapt to the growing demands for speed, efficiency, and security. The future will likely see a seamless integration of cloud, edge, and AI-driven computing to optimise performance across industries.
Hybrid Approaches: The Best of Both Worlds
Many organizations are not choosing between edge computing and cloud. Instead, they are adopting hybrid models that blend the benefits of both. This lets businesses handle urgent data on-site. They can also use cloud computing for big storage and analysis.
The Role of AI and 5G
AI and 5G networks will boost cloud and edge computing even more. AI will optimise data distribution between edge and cloud systems, improving efficiency. 5G will boost connectivity. It will cut down latency and improve edge computing.
Sustainability and Green Computing
As technology evolves, sustainability is becoming a priority. Companies are looking into data centres powered by renewable energy. They are also using optimised cooling systems and energy-efficient edge devices. This helps them lower their environmental impact.
Edge vs. Cloud: Choosing the Right Computing Model for the Future
When comparing edge computing vs cloud, it’s clear that each has its strengths and ideal use cases. Cloud infrastructure provides scalability and cost efficiency, making it suitable for data-heavy applications. In contrast, edge computing excels in low-latency, real-time processing scenarios. The future of computing models will balance cloud and edge technologies. This mix will use the strengths of both. As businesses and technology change, knowing these differences is key. It helps in making smart choices for infrastructure and application development.